A Supply-Chain Control Program assures that the ingredients, raw materials, and non-food chemicals you receive are safe and suitable for use. Supplier control is an essential element of a preventive food safety system. The program is built on ingredient specifications that are defined following a hazard analysis, criteria for supplier selection, a process for approving suppliers, development of supplier agreements, and verification activities to assure that the program is in place and effective.
The hazard analysis identifies biological, chemical, physical, and Economically Motivated hazards associated with an ingredient that requires a control to significantly minimize or eliminate the hazard at your facility or at the supplier. It is critical to know what ingredients pose a food safety risk and who will control the identified hazard. If your supplier is controlling the hazard, then you should understand how they are accomplishing this. The food safety hazards presented by the supply chain are related to both the amount of control you have over the sourcing of the ingredient and the amount of transparency that you have with respect to the food safety practices of ingredient suppliers.
Approval of suppliers and ingredients should take place before the ingredient is received in your facility. Supplier Verification activities include audits of the supplier’s facility, reviews of their HACCP or Food Safety Plan, and verification testing of the ingredient at the supplier or upon receipt.
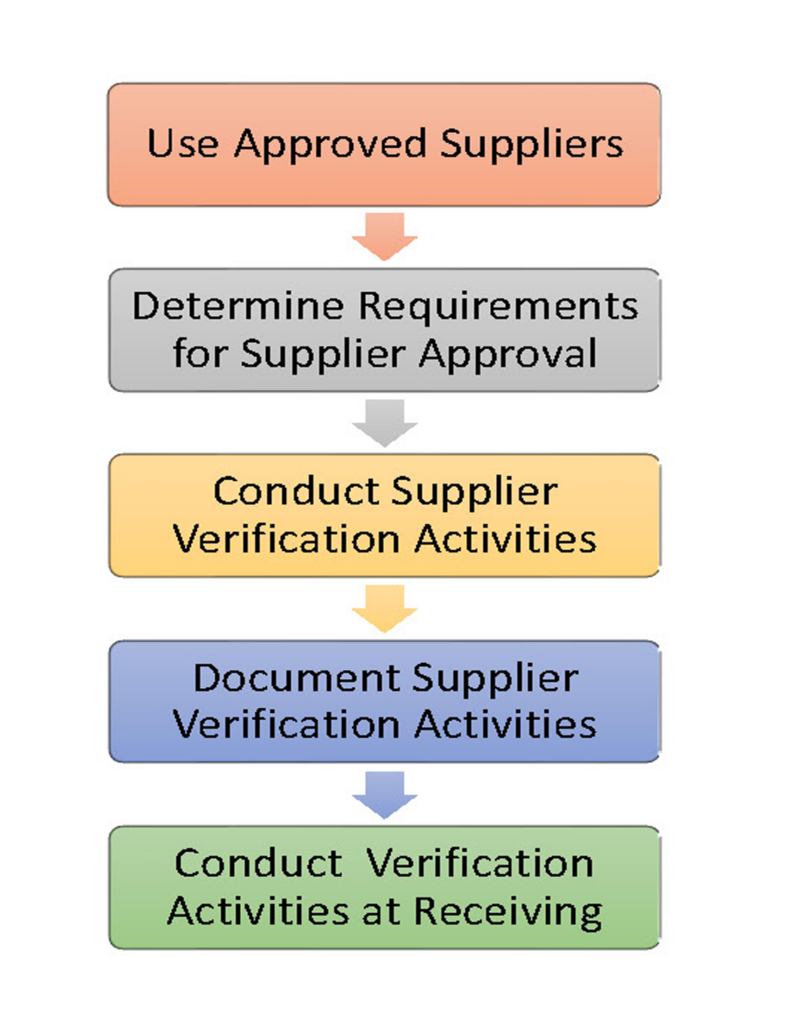
It is important to determine the ability and willingness of a supplier to meet your product specifications. A strong program is based on establishing a formal agreement with your supplier to ensure that they will share in the responsibility for food safety with respect to controlling hazards within their own facility. This may reduce the level of preventive controls needed by you upon receipt of the ingredient.
Your risk is lowest when every ingredient has a written specification detailing microbiological, chemical, and physical requirements as indicated by your hazard assessment and when each lot of ingredient is accompanied by a Certificate of Analysis (COA) reporting the results of appropriate verification testing from a trusted supplier. A robust in-bound receiving program with written procedures for reviewing COAs and documenting shipments with receiving records assures that each shipment meets your specification requirements. Even when other verification activities are in place, testing for hazards controlled by your supplier, at some designated frequency, provides additional evidence that supplier food safety systems are working. Your risk increases when you don’t require a COA for every lot purchased and do not require appropriate verification testing by the supplier or as part of your own receiving program.
Testing upon receipt may seem redundant when the supplier provides a COA. However, independent testing offers not only some assurance of the accuracy of the results reported on the COA, but also assurance that no adulteration of the ingredient has occurred between the time of analysis by the supplier and the time of receipt by the buyer. Verification of the supplier’s testing program as well as your own program should include corroboration that the laboratory performing the analyses is certified to conduct the tests and that methods are accredited and appropriate for testing the ingredients analyzed.
Good management of your suppliers will control microbiological, chemical, physical, Economically Motivated and food fraud hazards. For instance, as part of your Supply Chain Verification program, a review and approval of your supplier’s pathogen and allergen Preventive Control programs will minimize the risk that microbial contaminants and unlabeled allergens will enter your facility. This requires each supplier to have their own written programs. For ingredients you identify as having a particular pathogen concern, close the verification loop with an in-house program that screens statistically representative samples from each lot for the pathogen prior to use – either through a Preshipment Testing program or upon receipt.
The key to an effective Supply Chain Control Program is established policies and procedures and trusted suppliers with whom you are able to partner to prevent product safety issues.


