Use of Unapproved Food Additives – FDA’s Public Inventory
Any substance used or intended for use in food must be authorized by the FDA for use as a food additive under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act, unless the use of that substance is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by qualified experts or qualifies for an exemption.
As part of its on-going compliance activities, FDA conducts post-market activities to monitor the food supply for chemical contaminants. FDA identifies foods that contain a substance for which there is no authorization as a food additive and then reviews the regulatory status of this substance. FDA scientists analyze whether there is a basis to conclude that the intended use of the substance is GRAS or meets a
listed exception to the food additive definition. When FDA scientists determine that a substance is an unapproved food additive because it is not GRAS for its intended use (and does not meet a listed exception), they deem the additive to be unsafe and any food that contains the additive is adulterated.
On July 12, 2023, FDA released a public inventory of certain food ingredients that do not have GRAS status as determined by the agency and are therefore deemed unsafe. The inventory is a useful tool to assure the use of authorized ingredients.
The FDA Concludes Voluntary Pilot Program to Evaluate Alignment of Third-Party Food Safety Standards
with FSMA Rules
Food manufacturers may find that they are required to comply with one of the Global Food Safety Initiative standards in addition to the FDA’s Preventive Controls for Human Food or Produce Safety Rules. The FDA recently concluded a voluntary pilot program to evaluate alignment of private third-party food safety audit standards including BRC, FSSC22000, SQF and Global G.A.P. with applicable FDA regulations.
The pilot program was launched to help both FDA and industry gain a better understanding of whether these standards align with FDA regulations. Alignment between these standards may allow a company to structure their food safety plan to eliminate redundancy in their documentation and auditing programs.
Buyers and others in the food supply-chain often use third-party audits to assess the quality and safety of a product. Buyers, such as importers and receiving facilities, might stipulate an audit as part of a purchase agreement. In addition, three FSMA regulations – the Preventive Controls for Human Food rule, Preventive Controls for Animal Food (PC Animal Food) rule, and Foreign Supplier Verification Programs (FSVP) rule – allow for third-party audits to be used as supplier verification activities. Points of alignment would provide confidence that, in general, the third-party standards used to audit suppliers adequately address applicable FDA food safety requirements.
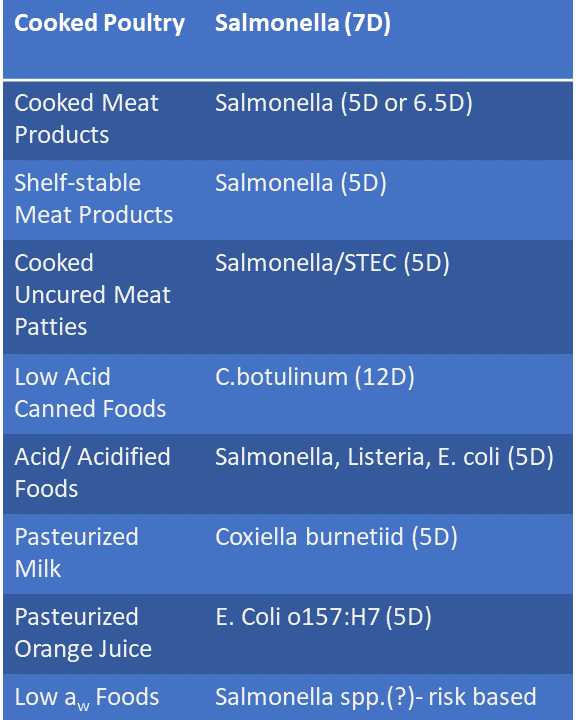
The results of the pilot program can be found in The FDA Concludes Voluntary Pilot Program to Evaluate Alignment of Third-Party Food Safety Standards with FSMA Rules. The FDA’s statements regarding alignment of the standards are referenced in the table below and apply only to the specified audit standards and addenda listed.
The reviews listed in the table focused on assessing third-party food safety standards and not the overall quality of the audit programs or qualifications of auditors. The FDA’s review and the findings from this pilot do not constitute an endorsement of any one food safety audit standard, or audits conducted under such standards. The FDA also adds a qualifying statement that third-party audits are not a substitute for FDA or state regulatory inspections for compliance with FDA regulations, including the Preventive Controls for Human Food Rule or the Produce Safety Rule.
| Third-Party Food Safety Audit Standard and Applicable Addendum | Scope Name |
|---|---|
| BRC Global Standard Food Safety plus the Global Standard Food Safety, Issue 9, Interpretation Guideline | Preventive Controls for Human Food (PCHF) |
| FSSC 22000 Scheme 5.1 for Food Manufacturing plus the FSSC 22000, Version 3 FSMA PCHF Report Addendum | Preventive Controls for Human Food (PCHF |
| SQF Food Safety Code: Food Manufacturing, Edition 9 plus the SQF Addendum for the Preventive Controls for Human Food | Preventive Controls for Human Food (PCHF) |
| GLOBALG.A.P. Integrated Farm Assurance – All Farm Base Crops Base – Fruit and Vegetables Checklist. Version 5.4-1- GFS plus the GLOBALG.A.P. Food Safety Modernization Act Produce Safety Rule Add-on Module Version 1.3 | Produce Safety Rule (PSR) *Did not include Subpart E, related to Agricultural Water (as applicable to non-sprout produce) or Subpart M, related to sprouts |